
Facile fabrication of core-shell polyelectrolyte complexes nanofibers based on electric field induced phase separation
Ma, Haoqin, Chen, Guangkai, Zhang, Jingnan, Liu, Yong*, Nie, Jun, Ma, Guiping*
Abstract:The core-shell polyelectrolyte complexes chitosan (CS)/hyaluronic acid (HA) nanofibers could be produced from electric field inducing phase separation during the progress of electrospinning. The morphology of core-shell nanofibers was supported using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and tran**ission electron microscopy (TEM). The presence of CS on the shell of the nanofibers was also verified by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) ****ysis as further evidence of core-shell formation. In the electrospinning process, the protonated CS molecules migrated in the direction of the electric field, whereas the ionized HA molecules migrated in the opposite direction. Methylthiazolydiphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay was employed to investigate the toxic and cytocompatibility with the possible application for tissue engineering scaffolds. The drug release from coreeshell nanofiber in vitro was investigated by UV spectrophotometry. The release profiles for coreeshell nanofibers showed more controlled and sustained release. while fibroblasts cells could still adhere to and proliferate on the drug-loaded coreeshell nanofiber membranes. The results implied that core-shell polyelectrolyte complexes CS/HA nanofibers encapsulating drugs have great potential in tissue engineering scaffolds.
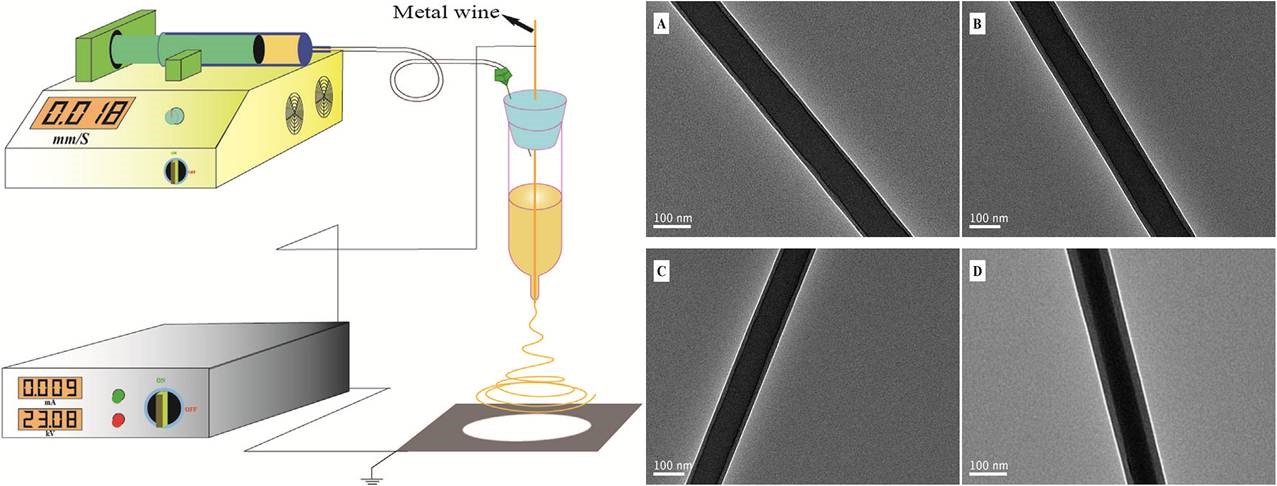
Fig. 1. Schematic representation of the electrospinning setup and TEM images of HA/CS nanofibers electrospun from different ratios of HA and CS: (A) 9/1, (B) 8/2, (C) 7/3, and (D) 6/4.
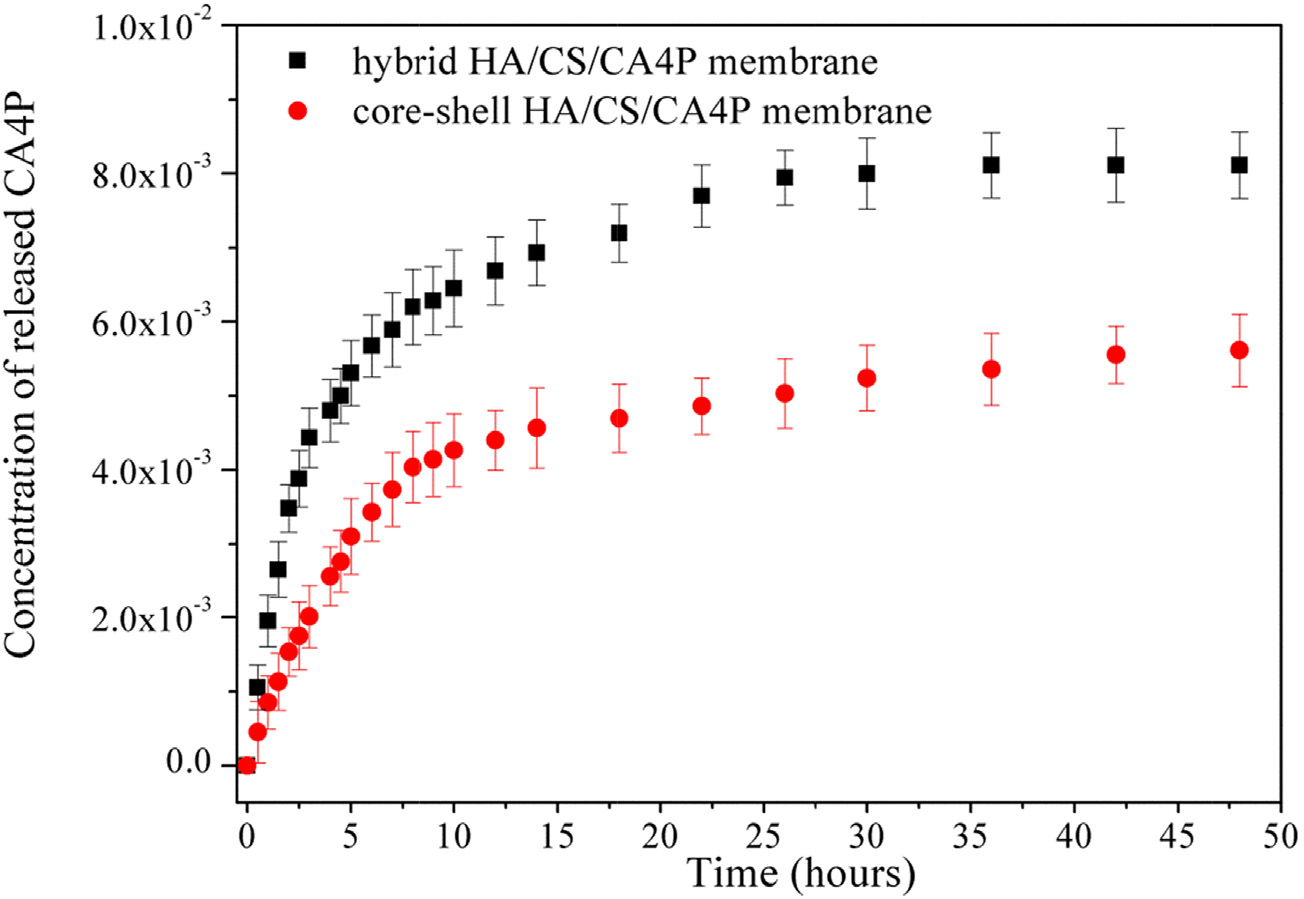
Fig. 2. Drug-release kinetic curves of hybrid HA/CS and coreeshell HA/CS nanofiber membranes