Main chain copolysiloxanes with terthiophene and perylenediimide units: synthesis, characterization and electrical memory
Zhen Chen, Tingjie Zhang, Yi Zhang, Zhongjie Ren, Jianming Zhang and Shouke Yan
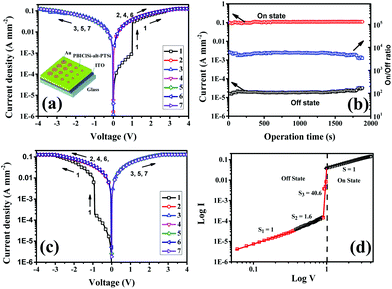
Abstract : A main chain donor–acceptor copolysiloxane named poly(N,N’-bis(dimethylsiloxane)propyl tetrachloro perylene tetracarboxylic acid diimide-alt-bis(dimethylsiloxane)-2,2`:5`,2``-terthiophene) (PBIClSi-alt-PTSi) was successfully synthesized, in which terthiophene donors and perylenediimide acceptors are connected with siloxanes. PBIClSi-alt-PTSi displays high thermal stability, which ensures its long-term stability for device operation. The calculated HOMO and LUMO energy levels of PBIClSi-alt-PTSi are mainly located on terthiophene and perylenediimide moieties, respectively. A fabricated memory device with the configuration of ITO/PBIClSi-alt-PTSi/Au(Al) shows nonvolatile write-once-read many-times (WORM) memory characteristics. Its turn-on threshold voltage is quite low (ca. 1.0 V), meanwhile the on/off current density ratio is around 6 × 103 under ambient atmosphere. As far as we know, this is the first example of a main chain donor–acceptor copolysiloxane used as a memory device. And the low turn-on threshold voltage of 1.0 V may be caused by the high flexibility of Si–O–Si. Furthermore, the progression of the ITO/PBIClSi-alt-PTSi/Au device from a low to high conductivity state is detected by current sensing atomic force microscopy for the first time. At the threshold voltage, the topology of the PBIClSi-alt-PTSi films displays an obvious change due to the arrangement of molecular chains.