J Appl Polym Sci. 2016, 133, 43488. Published online, DIO: 10.1002/app.43488.
Shicheng Qi, Hongrui Wang, Guo han, Zhen Yang, Xiao A Zhang*, Shengling Jiang, Yafei Lu.
ABSTRACT
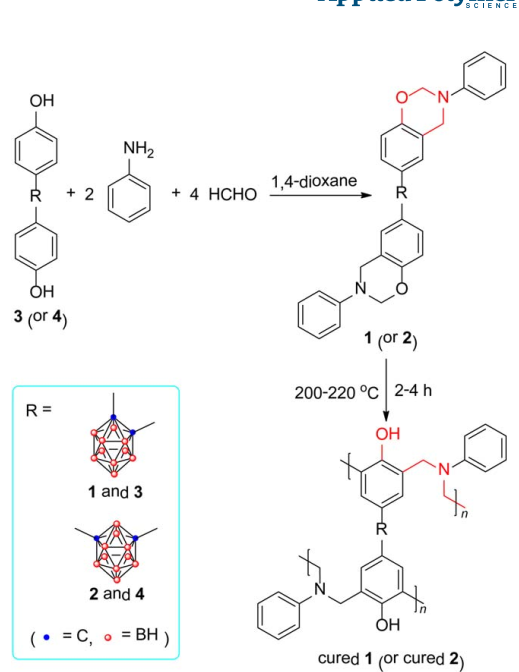
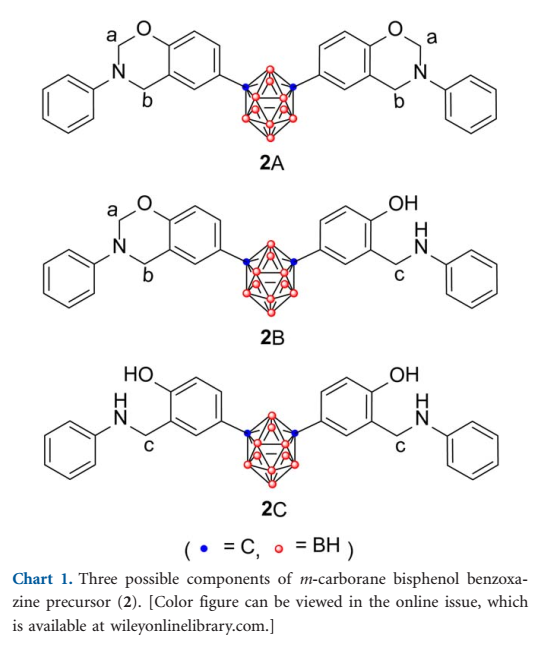
Two benzoxazine precursors bearing carborane moiety (1 and 2) were designed and synthesized successfully by the Mannich reaction of corresponding carborane bisphenol (3 and 4) with aniline and formaldehyde in 1,4-dioxane. The obtained precursors were characterized by using multiple spectroscopic techniques including GPC, FTIR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, and 11B NMR. Nonisothermal DSC studies showed that precursor 1 owned lower apparent activation energies (Ea) than 2. The optimum curing processes of benzoxazine precursors were also obtained on the basis of DSC data. TGA ****yses manifested that the incorporation of carborane moiety endowed the obtained benzoxazine resins (cured 1 and 2) with excellent thermal stability and unique thermo-oxidative stability. The Td data showed that the initial degradation of both cured 1 and 2 under nitrogen and air was postponed to some extent owing to the shielding effect of carborane moiety on adjacent organic fragments. At higher temperature three-dimensional polymer networks with B-O-B and B–C linkages were formed as chars by the reaction of carborane cage with atmospheric moisture, degradation products such as phenolic hydroxyl, and oxygen (under air). Under nitrogen this network hindered the motion of radicals formed at elevated temperature and thus inhibited further polymer degradation processes. While under air, the formed boron-rich networks could hardly be further oxidized into carbon dioxide so that the carborane-containing benzoxazine resins also showed very high char yields.