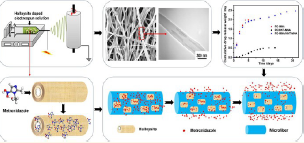
Electrospun Microfiber Membranes Embedded with Drug-Loaded Clay Nanotubes for Sustained Antimicrobial Protection.
Jiajia Xue , Yuzhao Niu , Min Gong , Rui Shi , Dafu Chen , Liqun Zhang , and Yuri Lvov
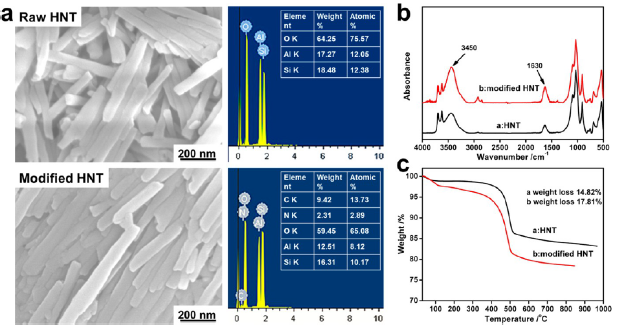
Guided tissue regeneration/guided bone regeneration membranes with sustained drug delivery were developed by electrospinning drug-loaded halloysite clay nanotubes doped into poly(caprolactone)/gelatin microfibers. Use of 20 wt % nanotube content in fiber membranes allowed for 25 wt % metronidazole drug loading in the membrane. Nanotubes with a diameter of 50 nm and a length of 600 nm were aligned within the 400 nm diameter electrospun fibers, resulting in membranes with doubling of tensile strength along the collector rotating direction. The halloysite-doped membranes acted as barriers against cell ingrows and have good biocompatibility. The metronidazole-loaded halloysite nanotubes incorporated in the microfibers allowed for extended release of the drugs over 20 days, compared to 4 days when directly admixed into the microfibers. The sustained release of metronidazole from the membranes prevented the colonization of anaerobic Fusobacteria, while eukaryotic cells could still adhere to and proliferate on the drug-loaded composite membranes. This indicates the potential of halloysite clay nanotubes as drug containers that can be incorporated into electrospun membranes for clinical applications.