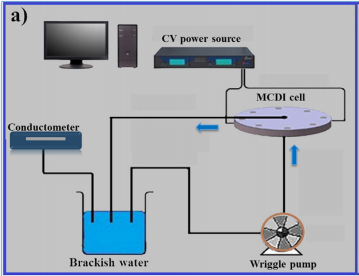
A cross-linked quaternised polyvinyl alcohol (QPVA) membrane, modified with glycidyltrimethylammonium chloride and glutaraldehyde, was used as an anion exchange membrane for membrane capacitive deionization (MCDI). The microstructure and properties of the membrane were characterized by elemental ****ysis, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, differential scanning calorimetry, thermogravimetric ****ysis and scanning electron microscopy. The electrochemical influences of QPVA on activated carbon electrode were examined by cyclic voltammetly and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. And electrosorption performance of the composite electrode was investigated by NaCl capacitive deionization test. The results showed that the structure order degree, ion exchange capacity and moisture content of QPVA decreased with an increasing degree of cross-linking. Accompanied by lower electric resistance, the carbon electrode with a compressed membrane exhibited a higher specific capacitance (180 F/g) than the coated membrane (155 F/g). The cross-linked QPVA membrane (0.8 mL 5 wt.% glutaraldehyde solution and 0.5 g QPVA) was compressed onto an active carbon (AC) electrode and provided the optimum conditions of deionization with the adsorption capacity of 15.6 mg/g, and the adsorption kinetics of NaCl onto the composite electrodes was affirmed by Lagergren's pseudo-first-order model. (C) 2014 Elsevier BM. All rights reserved.
DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2014.09.024