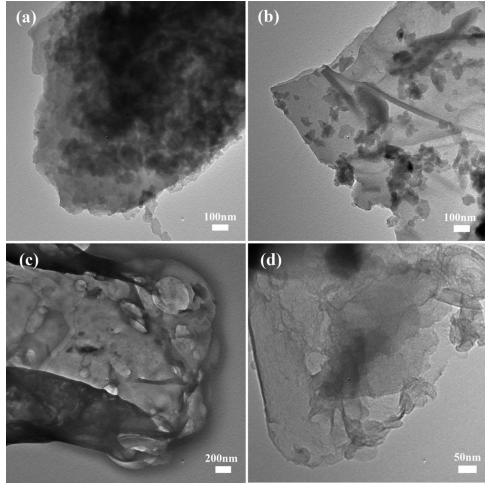
Lithium-ion supercapacitor (LIC) was fabricated with nanosheet Li4Ti5O12 (LTO) as the negative electrode and activated-nitrogen-doped graphene-basedaerogel composites (a-NGA) as the positive electrode. The structure, morphology, and pore-size distribution of a-NGA was characterized by SEM, TEM, XRD, TGA, XPS, and nitrogen adsorption-desorption method. Electrochemical properties of a-NGA and nanosheet LTO were studied by galvanostatic charge and discharge test. The results indicated that KOH activation effectively modified the porous structure of NGA and improved its specific surface area to achieve better porosity, thereby enhancing the electrochemical properties. The assembled LIC provide a maximum energy density of 70 Wh kg(-1) with the power density of 200 W kg(-1) in a voltage of 1-3 V, and still retained an energy density of 21 Wh kg(-1) at a high power density of 8000 W kg(-1). More significantly, its exhibits good cycling stability with retention of 64% after 10000 cycles at a high current density of 1.5 A g(-1). (C) 2016 The Electrochemical Society. All rights reserved.