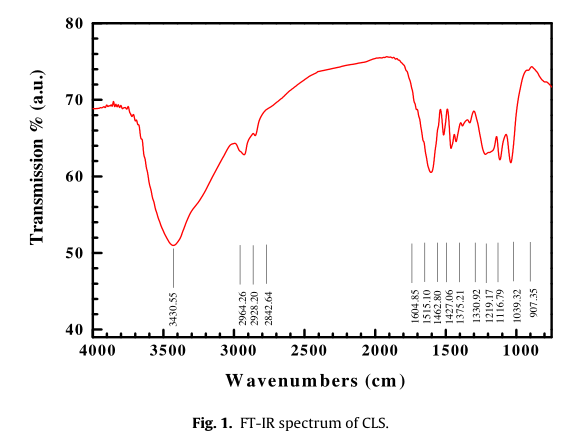
The corrosion inhibition of calcium lignosulfonate (CLS) for Q235 carbon steel in saturatedCa(OH)2+ 0.1 mol/L NaCl solution was studied by means of weight loss, polarization, fluorescencemicroscopy (FM), scanning electron microscopy/energy dispersive spectrometry (SEM/EDS), microscopicinfrared spectral imaging (M-IR) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). For the steel in simulatedconcrete pore solution (pH 12.6), an increase of Ebvalue and a decrease of icorrvalue occurred with dif-ferent concentrations of CLS. The optimal content of CLS was 0.001 mol/L at which the inhibition ratewas 98.86% and the Ebvalue increased to 719 mV after 10 h of immersion. In mortar solution and inreinforced concrete environment, CLS also showed good inhibition for steel. The preferential adsorptionof CLS around pits was detected by M-IR. The result illustrates that at the early stage the adsorption ofCLS was heterogeneous and CLS may have a competitive adsorption with chloride ions at the active sites,which would be beneficial for decreasing the susceptibility of pitting corrosion. After the pre-filmingtime, an intact adsorption CLS film formed on carbon steel surface. The adsorption between CLS and cal-cium presented as Ca O S bonds. The adsorption of CLS on carbon steel surface occurred probably byboth physisorption and chemisorption.