Xiaoyu Gu, Wenxiang Sun, Jia Guo, Xiangxing Bu, Hongfei Li, Sheng Zhang*, Jun Sun*. Fabrication of hydrotalcite containing N/P/S and its ternary synergistic efficiency on thermostability and fire resistance of ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA). Journal of Vinyl & Additive Technology. 2018. 25(3): 255-261.DOI: 10.1002/vnl.21684
https://doi.org/10.1002/vnl.21684
Abstract
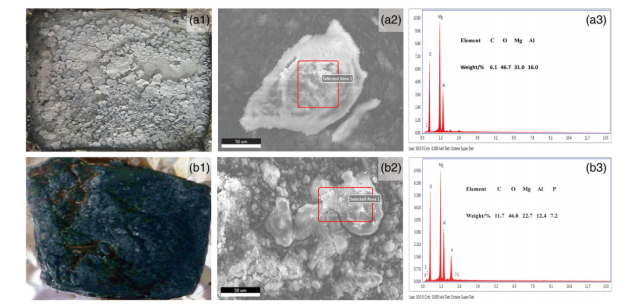
Nitrate intercalated hydrotalcite (NO3−‐HTC) was first prepared as precursor; a schiff base derivative containing N, P, and S was synthesized and its structure was characterized. Later the schiff base derivative was used as intercalation to replace NO3−in hydrotalcite. The final product was schiff base derivative intercalated hydrotalcite, which was named as benzaldehyde–taurine–hypophosphorous (BTP)‐HTC. The results showed both NO3−‐HTC and BTP‐HTC can effectively improve the flame retardant and thermostability of ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA). In cone calorimeter test, the peak heat release rate of EVA was 1421.2 kW/m2 and reduced sharply to 746.1/584.5 kW/m2 for 20 wt% NO3−‐HTC/BTP‐HTC adding, respectively. At same time, the total heat release was also decreased from 120.6 MJ/m2 for EVA to 81.0/70.0 MJ/m2, respectively. Morphology observation and composition ****ysis by scanning electron microscopy (SEM)/X‐ray spectroscopy (EDS) documented the residue left after combustion of EVA/NO3−‐HTC was just ash containing Mg and Al; but for EVA/BTP‐HTC, coherent char layer containing Mg, Al, and P was left. Thermogravimetric ****ysis indicated that the thermal degradation of EVA was prolonged by either NO3−‐HTC or BTP‐HTC; and char content was kept to 8.6% and 11.0%, respectively. The whole results documented either NO3−‐HTC or BTP‐HTC improved the combustion behavior and thermostability of EVA, and BTP‐HTC showed excellent effect. J. VINYL ADDIT. TECHNOL., 25:255–261, 2019. © 2018 Society of Plastics Engineers