In Situ ice template approach to fabricate 3D flexible MXene film-based electrode for high performance supercapacitors --- Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30, 2000922.
Peng Zhang, Qizhen Zhu, Razium Ali Soomro, Shiyu He, Ning Sun, Ning Qiao, Bin Xu*
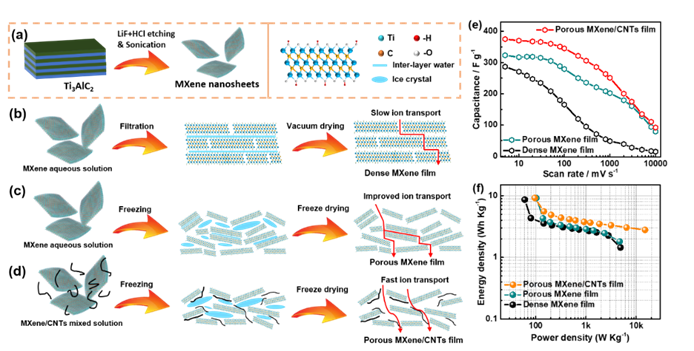
MXenes with metallic conductivity, high pseudo‐capacitance and 2D structure, are promising flexible electrode materials for supercapacitors, but suffer from the restacking issue, which hinders ion accessibility and causes sluggish ion kinetics. Herein, a simple in situ ice template strategy is proposed to fabricate free‐standing, flexible 3D porous Ti3C2Tx/carbon nanotubes (CNTs) film (3D‐PMCF) by freeze‐drying Ti3C2Tx‐based hydro‐films without any postprocessing. During the freeze‐drying process, **all ice grains are in situ transformed from the residual water molecules in the Ti3C2Tx interlayer and then act as a self‐sacrifice template to construct a 3D porous network. CNTs introduced in the hydro‐film increase the amount of interlayer water and the resultant porosity. The 3D structure of Ti3C2Tx significantly increases the exposed surface active sites and accelerates the ion transport, meanwhile maintaining good flexibility. Consequently, the flexible 3D‐PMCF film delivers a capacitance of 375 F g−1 at 5 mV s−1 and retains 251.2 F g−1 at 1000 mV s−1 with excellent cycling stability, much superior to the conventional densely stacked Ti3C2Tx film. Being assembled into a symmetric supercapacitor, an energy density of 9.2 Wh kg−1 is realized. This work demonstrates a simple and efficient route for constructing high‐performance and flexible 3D MXene film electrodes for supercapacitors.